What is Zero Valent Iron (ZVI) and how can it solve complex remediation challenges?
Across industrial sites, former manufacturing plants, and legacy waste areas, soil and groundwater contamination remains a persistent challenge. Chlorinated solvents seep through fractured bedrock, heavy metals linger in sediments, and nitrates travel silently through aquifers. Traditional pump-and-treat systems often prove costly and slow, leaving engineers and regulators searching for solutions that are both effective and sustainable. One material—Zero Valent Iron (ZVI)—has emerged as a proven technology to directly transform harmful contaminants into harmless or stable forms, right where they are found.

Unlocking the potential of granular ZVI
Introduction
Zero Valent Iron (ZVI) is metallic iron in its elemental form (Fe⁰) that can degrade or immobilize environmental contaminants through oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Since the early 1990s, when it was first deployed in permeable reactive barriers (PRBs), ZVI has evolved into a versatile tool for addressing a wide range of soil and groundwater contamination problems. Today, it is recognized globally as a reliable and sustainable solution for chlorinated solvents, heavy metals, nitrates, and other pollutants.
Chemical principles of ZVI reactivity
Understanding the redox mechanisms behind contaminant reduction
The effectiveness of ZVI comes from its ability to act as a strong reducing agent. When in contact with water and contaminants, Fe⁰ oxidizes to Fe²⁺ or Fe³⁺ while the contaminant undergoes reduction.
Example reaction for chlorinated solvent dechlorination:
Fe⁰ + R–Cl + H⁺ → Fe²⁺ + R–H + Cl⁻
Electron transfer pathways:
- Direct electron transfer from the iron surface to the contaminant molecule.
- Indirect transfer via hydrogen produced during iron corrosion.
By-products:
- Dissolved ferrous/ferric ions (Fe²⁺, Fe³⁺)
- Iron hydroxides and oxides, which can adsorb other contaminants
- Hydrogen gas, which may stimulate beneficial anaerobic biodegradation
Impact of particle size:
- Granular/microscale ZVI: Lower reaction rate, but longer service life.
- Nano-ZVI: High reactivity due to increased surface area, but shorter operational life unless stabilized.
Types of ZVI
Comparing granular, microscale, nanoscale, and modified iron
- Granular ZVI (GZVI): Millimeter-scale particles, best suited for long-term applications in PRBs.
- Microscale ZVI (mZVI): 10–100 µm particles, used for slurry injections or in-situ soil mixing.
- Nanoscale ZVI (nZVI): <100 nm particles with very high reactivity for rapid hotspot treatment.
- Modified ZVI: Includes bimetallic particles (e.g., Fe/Pd, Fe/Ni) and sulfidated ZVI for enhanced selectivity and reduced passivation.

Applications in environmental remediation
From soil cleanup to groundwater and industrial water treatment
ZVI is used in a variety of environmental contexts, each requiring specific engineering design:
Soil remediation:
- Destruction of chlorinated solvents such as TCE and PCE.
- Reduction of toxic Cr⁶⁺ to less soluble Cr³⁺.
- Immobilization of arsenic and other heavy metals.
Groundwater remediation:
- Permeable reactive barriers that passively intercept contaminant plumes.
- Direct injection into source zones for rapid treatment.
Surface water and industrial effluents:
- Nitrate, arsenic, and selenium removal.
- Integration into stormwater polishing systems.
Specialized cases:
- Acid mine drainage treatment.
- PFAS degradation research when paired with oxidants or heat.

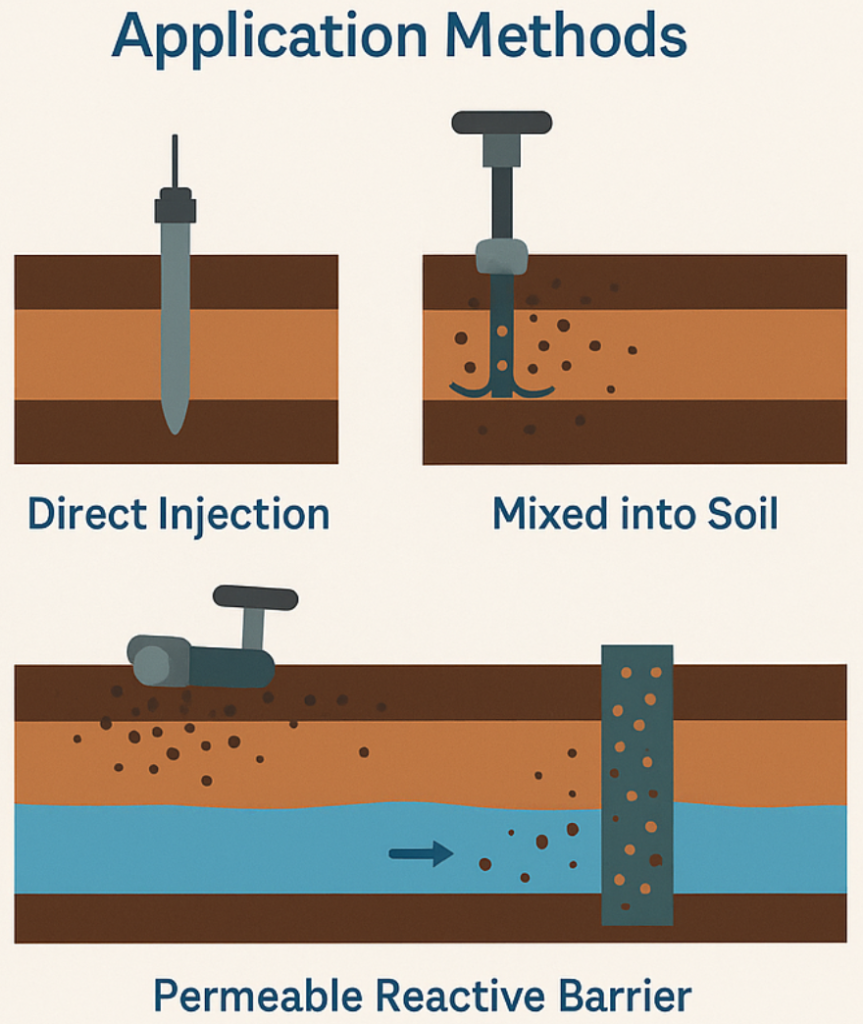
Implementation methods
Engineering approaches for in-situ and ex-situ ZVI deployment
Engineers can apply ZVI using different strategies, each optimized for site-specific conditions:
- Permeable reactive barriers (PRBs): Excavated trenches filled with GZVI, designed for the required contaminant residence time.
- Injection: Direct-push or recirculation well delivery of mZVI or nZVI slurries.
- Soil mixing: Mechanical blending of ZVI into contaminated soils for source treatment.
- Reactor-based systems: Packed-bed or fluidized ZVI reactors for ex-situ treatment of contaminated water.
Advantages and limitations
Balancing performance, longevity, and operational constraints
Advantages:
- Effective against both organic and inorganic contaminants.
- Passive operation in PRBs with minimal maintenance costs.
- Environmentally safe by-products in many cases.
Limitations:
- Surface passivation from oxide or carbonate formation, reducing reactivity.
- Limited mobility of larger particles in fine-grained soils.
- Gas generation that may require venting in low-permeability zones.
How Winoa Peerless can help
Delivering high-quality granular ZVI with technical support
Winoa (formely Peerless) offers high-quality granular Zero Valent Iron tailored for consistent, reliable performance in environmental remediation projects. Our ZVI is characterized by:
- Controlled particle size distribution.
- High purity for predictable reactivity.
- Optimized surface area for enhanced contaminant reduction.
Typical uses include permeable reactive barriers, direct-push injection, and soil blending for chlorinated solvents, nitrates, and heavy metals. We supply in bulk packaging for large-scale projects and provide technical guidance to ensure efficient, cost-effective integration into remediation designs.
Conclusion
Why ZVI remains a key technology for sustainable remediation
Zero Valent Iron is a proven, adaptable technology that plays a central role in modern soil and groundwater remediation. Whether deployed in long-lasting PRBs or as a rapid-response injection material, ZVI can address complex contamination challenges effectively and sustainably. With proper engineering design, quality product selection, and field expertise, it offers both immediate and long-term environmental benefits.
Learn more about our ZVI solutions
Download the full Winoa Peerless Zero Valent Iron brochure to see product specifications, performance data, and application guidelines.








